![]()
HIV and TB
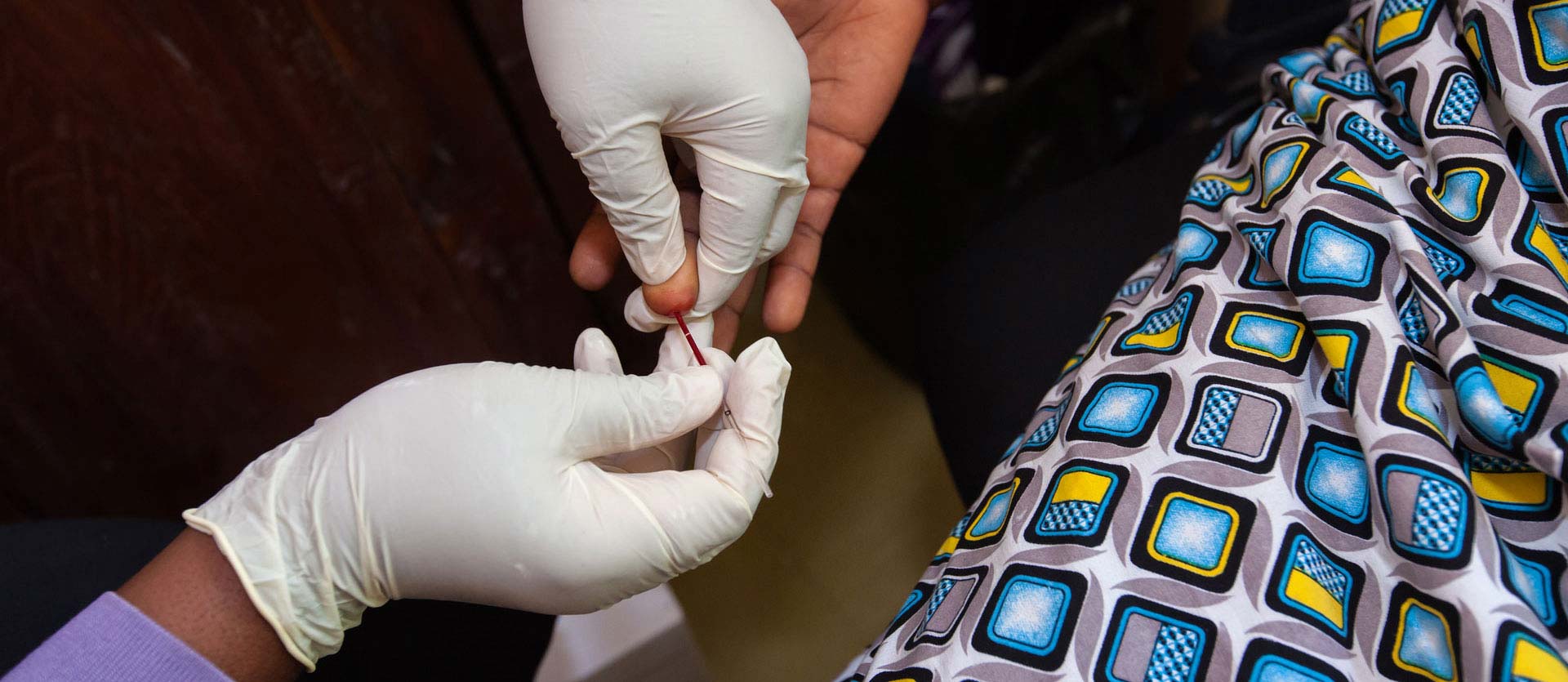
While steady progress has been made in the HIV pandemic, women are still disproportionately affected in many countries where MCSP works, especially adolescent girls and young women. In sub-Saharan Africa, women account for 56% of new HIV infections among adults. The Program is contributing to the global goal of ending the AIDS and TB epidemics by increasing access to prevention, treatment, care and support services. We assist governments throughout the region to ensure that HIV testing and treatment is afforded to women and their children when accessing MCSP-supported maternal and child health services.
In Namibia, MCSP worked to advance the US President’s Emergency Plan for AIDS Relief’s (PEPFAR) Blueprint: Creating an AIDS Free Generation, and USAID’s objectives for the country and the Agency’s global goals to prevent maternal and child deaths. Beginning in 2014, MCSP supported Namibia’s Ministry of Health and Social Services (MOHSS) to strengthen:
- The continuum of care from households and communities to health facilities by improving and institutionalizing the community health worker (CHW) cadre and the national Health Extension Program (HEP);
- Access to and uptake of comprehensive, youth-friendly HIV services by priority populations;
- Programmatic commitment to and emphasis on reaching and supporting young people with HIV services; and
- Program efficiencies through innovation and greater integration of existing HIV/TB and RMNCAH services, including focuses on nutrition and WASH.
MCSP also supported the MOHSS/Health Information and Research Directorate in the strategic enhancement and integration of the country’s fragmented Health Information System (HIS), and to improve data quality as well as its effective and strategic use for decision-making at all levels.
In Nigeria, MCSP provided technical assistance to US government-funded HIV testing services implementing partners to scale up and evaluate partner notification services (PNS), a highly effective approach to diagnosing and treating a HIV and other sexually transmitted infections. The Program also developed a learning resource package to support facility-based implementation and standardization of PNS in Nigeria. This package included: implementation materials; monitoring and evaluation tools; standard operating procedures; information, education, and communication materials; and tools for ongoing mentorship.
In Haiti, MCSP worked to strengthen the quality of HIV prevention, treatment, care and support services in 42 PEPFAR-supported facilities, and provided HIV testing services in four additional facilities. MCSP focused on supporting the increased efficiency of HIV testing in 42 facilities to better monitor adherence and retention of clients on ART, and prevent treatment failures/resistance to ART. Gender-specific barriers to uptake and adherence to treatment were addressed through ensuring peer education and support are culturally relevant. The Program also supported community-based services – such as distribution of antiretroviral therapy (ART) – with a focus on retention and care for all people living with HIV in MCSP areas.